GANGLION CYST

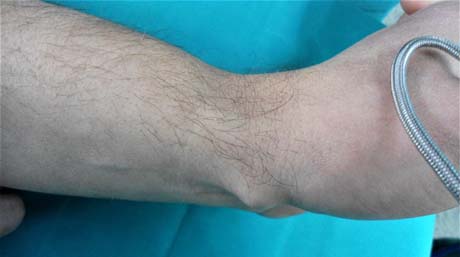
Ganglion is the most common benign clinical entity that concerns the area of the wrist, its spine or palmar surface.
Ganglion contains a transparent gel, which comes either from the bones of the wrist or from the handles of the tendons of the hand.
The size of the ganglion may change over time and the activity of the individual (manual labor).
It may also appear in other parts of the knee such as the fingers of the hand, the foot and the knee.
ETIOLOGY
The cause of the disease has not been fully elucidated to date. It occurs more often in people who have manual activity but can also appear
in people who do not particularly strain their upper limb. In patients suffering from autoimmune diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, gouty arthritis, etc.), the incidence of ganglion is higher compared other people.
CLINICAL EVALUATION
- If ganglion can be associated with malignancy
- The pain and perhaps the tingling in the wrist and hand
- The aesthetic factor especially in women if ganglion has large dimensions
affinity with nerve.
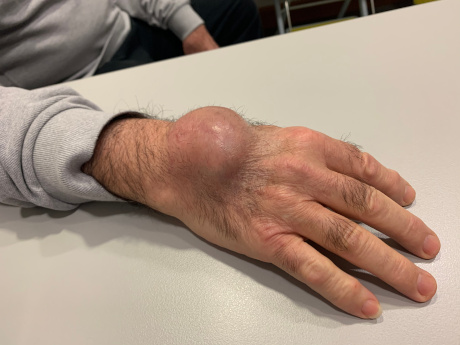
Large ganglion in the dorsal surface of the wrist, apart from the pain it causes to the patient, is also an aesthetic problem.


