NECK PAIN
The neck is the part of the body which connects the shank to the head. The cervical spine consists of seven vertebrae and is the most mobile part of it. Strong muscular and ligamentous structures adhere to the vertebrae creating a strong anatomical structure such that it can meet the extremely high demands of the region during the life of man.
X-ray cervical spine: normal appearance
The neck pain is not a disease but a clinical entity that actually describes the symptom that is the pain of neck and should be done the necessary investigation to ascertain the causes of pain.
Also the term cervical syndrome describes a range of clinical conditions that concern the patient but without this term to indicate the reasons for the problem.
For the effective therapeutic approach the Orthopaedist should primarily been clearly diagnosed the cause of a problem. Without the precise identification of the problem will not be effective and the patient's treatment.
ETIOLOGY
MUSCLE CAUSE
Muscle causes are the most common cause of pain in the neck in his youth. The long preoccupation with the computer and often in the wrong posture of the head and neck are the main cause of growth of muscle spasms in the neck muscles (trapezius muscles, short paraspinal muscles, etc.) and indirectly cause straightening of the cervical spine, loss ie the normal position of the neck lordosis. The result thereof is the pain challenge most often chronic nature.
In muscle causes included the muscle torticollis, clinical entity in which predilection spasm of muscle groups (sternocleidomastoid muscle), from only one side of the neck without the patient may turn the head because of the intense pain. This condition is benign and transient, and with proper treatment subsides in the next 7-10 days.
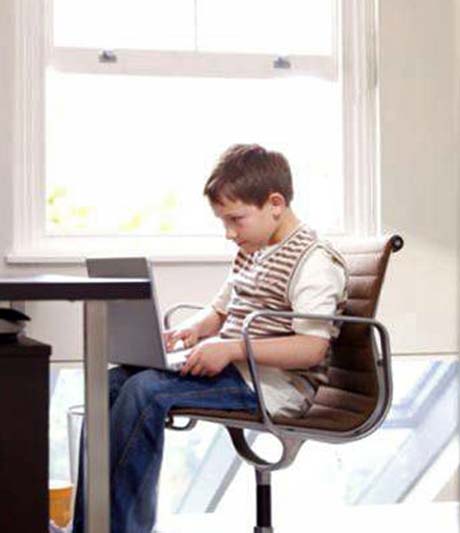
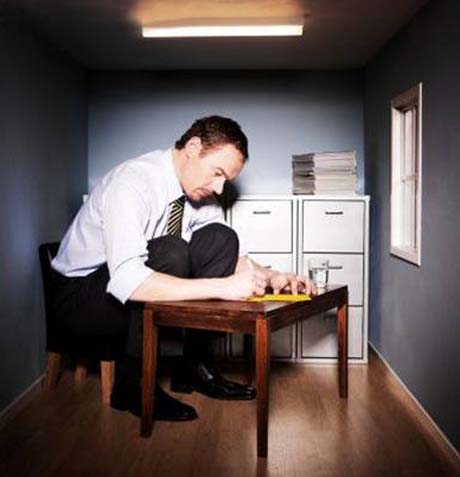



Prolonged wrong posture and neck during the work on the computer or office is the primary cause of pain in the neck
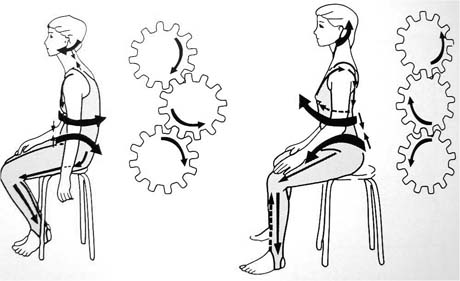
Left: poor posture and torques of the forces applied to the vertebrae
Right: the correct posture. We observe the normal torques of the forces applied to the vertebrae is exactly opposite in relation to the wrong attitude.
This implies that prolonged and long adopting wrong posture especially during working disrupts biomechanics of the spine entirely
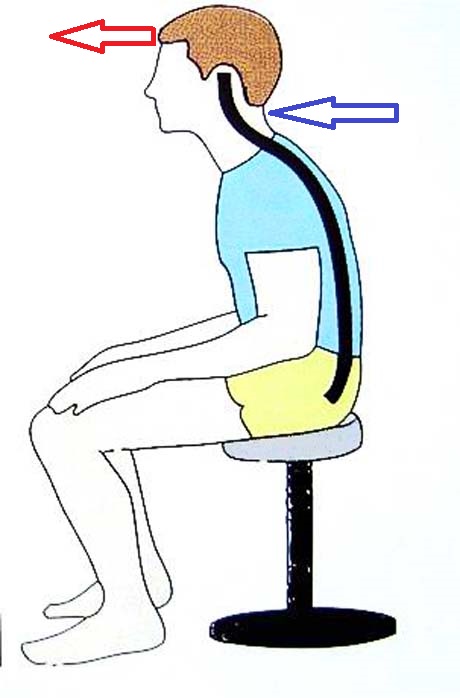
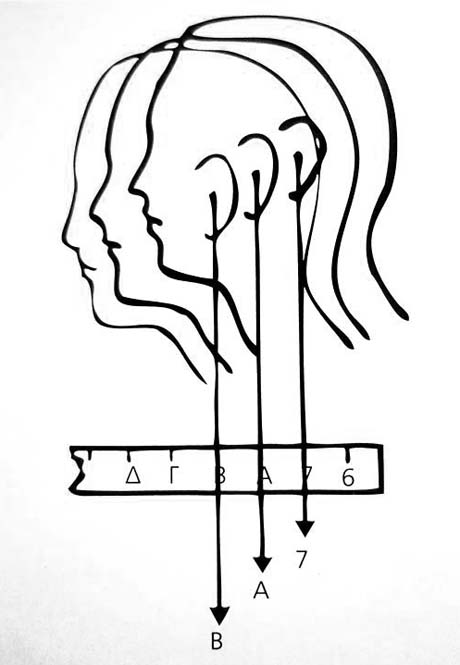
Poor posture of the torso and head causes shift forward of it which in the long term is a cause of neck problem

The neck can be likened to the hoist indicating thereby the size of the loads is forced to lift improper attitude that
Straightening of neck vertebrae due to chronic muscle spasm
Spinal stenosis due to reverse of normal cervical lordosis and bulging of the intervertebral discs
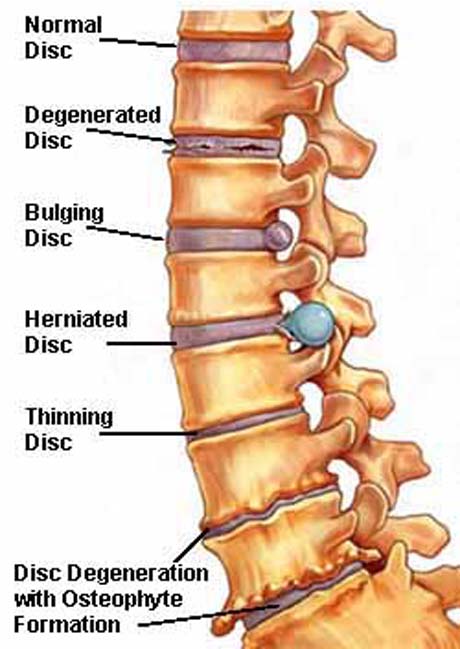
CAUSES DUE TO THE VERTEBRAE AND INTERVERTEBRAL DISCS
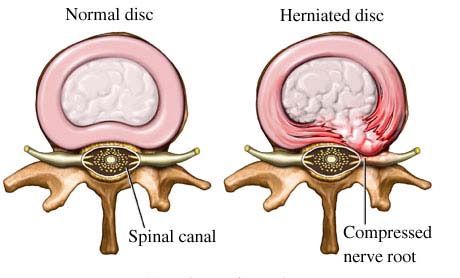
The causes related to the intervertebral discs occur in all age groups with a growing trend at older ages. As in the lumbar and cervical so between the vertebrae are intervertebral discs which act as shock absorption system of the spine and of increased overall mobility protect the noble structures such as the spinal cord and nerve strains that emerge from this .
The herniated intervertebral disc in the neck usually created
- prolonged small loads exerted wrong way up on him (most common cause).
- or very large load as abrupt application of large forces eg in a car accident, sports injury or attempt cargo support to the head or neck.
After age 40 the intervertebral disc gradually loses height resulting in the interval between the adjacent vertebrae but decreases creating thereby stress the joints between the vertebrae and growth conditions osteophytes and spondylitis which is another cause of neck pain.
Magnetic resonance imaging (sagittal section) illustrating multiple herniations intervertebral disc (red circle), which press the neural elements
Magnetic resonance imaging (cross-section) illustrating the pressure on the spinal cord of prolapsed intervertebral disc
SYMPTOMS
The symptoms that the patient is may be mild and well tolerated and as audible and intolerably. It can last from a few days to several weeks and months. Local may occur in the neck or to reflect on the shoulder, the shoulder or upper limb. The patient may report pain during limited anatomical movements, rest pain or even pain during night which does not allow him to sleep.Also the appearance of numbness or tingling sensation on the shoulder or hand complements the clinical symptomatology of the patient. The headache is finally another clinical entity that may be due to problems in the neck.
DIAGNOSTIC APPROACH
The clinical examination made by the Orthopaedic surgeon will record
- the condition of the muscle groupsexistence spasm,
- painful pressure,neck range of motion,
- sensation,tendon reflexes upper limbs (biceps, triceps, radial)
- muscular power control of the upper limb patient compared to healthy,
- investigating retroreflecting pain in the upper end or head (tension headache).
The radiological examination (X-ray), of the neck will give information on Orthopaedic surgeon regarding the state of bone structures - vertebrae and their relations with their -stenosis intervertebral discs. Also evaluated and the physiological lordosis of the cervical spine or the existence of straightening it.
X-ray of the neck: Straightening of the cervical spine.
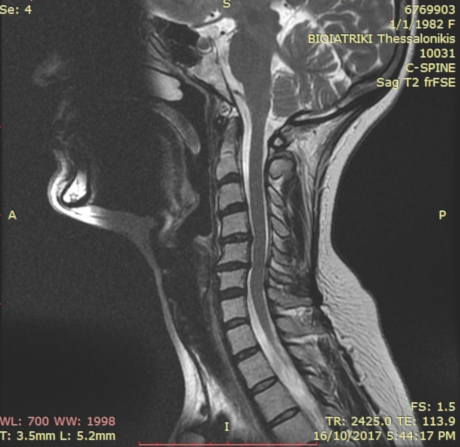
MRI of the cervical spine illustrating intense straightening occurring in women 36 years. The patient reports persistent neck pain
X-ray of the neck: spondyloarthropathy cervical spine with osteophytes appearance, altered shape, reduced intervertebral spaces in a patient aged 76 years
CT (with 3D reconstruction) and MRI are modern diagnostic methods which give highly detailed anatomical information to the physician to investigate the cause of the problem.
Computed tomography with three-dimensional reconstruction provides excellent information on the structure of the spine in place.
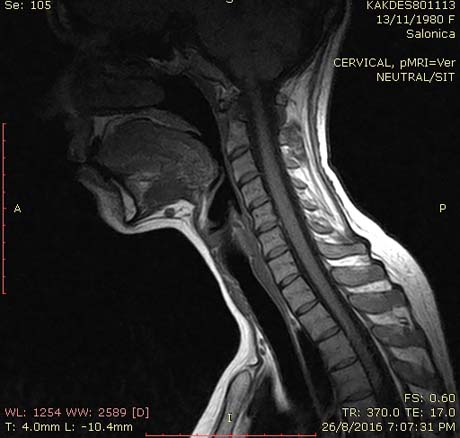
MRI (sagittal section): large herniated intervertebral disc (red circle), pressing the spinal cord causing severe pain to the patient that reflects the upper limb
Magnetic resonance imaging (cross-section): major herniated intervertebral disc which presses the exiting nerve root left
Electromyography of the upper limb is the sometimes an indispensable diagnostic tool for assessing the condition of the nerves and the investigation of the cause of pain. The examination is conducted by qualified neurologist.


