FLATFOOT IN CHILDREN
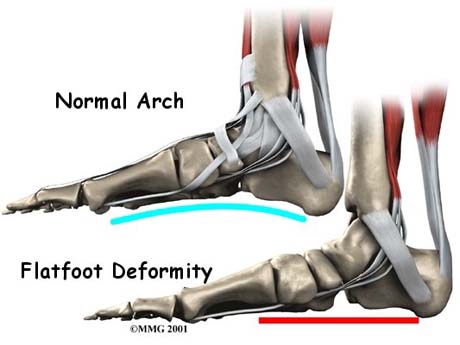
΄Flatfoot’ is describe a foot shape in which the medial longitudinal arch is depressed toward the ground. When a child with flexible flatfoot stands, the arch of the foot disappears. Upon sitting or when the child is on tiptoes, the arch reappears. Although called "flexible flatfoot," this condition always affects both feet.
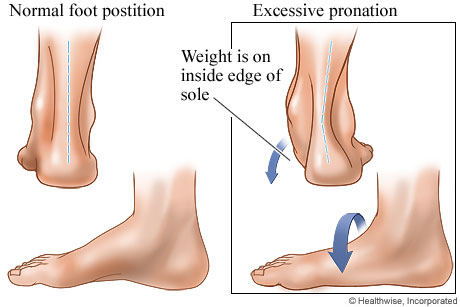
Flexible flatfoot is common in children. Parents and other family members often worry needlessly that an abnormally low or absent arch in a child's foot will lead to permanent deformities or disabilities. Flexible flatfoot is usually painless and does not interfere with walking or sports participation. Most children eventually outgrow it without any problems. Often accompanied by a turn of the heel to the outside and called pes planovalgus.
Flatfoot in boy 11 years old. The arch of the foot does not exist
The heels are beginning to be inclined outwardly. Pes planovalgus
Flat foot Types
- Flexible flatfoot
- Flexible flat foot combined with a short Achilles tendon
- Rigid flat foot
The flexible flatfoot is 2/3 of the entire flat foot in adults and in children the percentage is higher and usually does not cause clinical problems. It causes pain in children and not usually affect their participation in sports. It is considered that this type of flat foot is a variation of the normal foot and not a pathological clinical entity.
Most children born with little or no arch. The muscles and the joints loose form that is physiologically and operate harmoniously.
During the development of the child the soft tissues in the leg mature and 'tightening, gradually creating the arch - usually after the age of five years;.
If flatfoot continue during adolescence or adulthood, the individual may report pain in the leg.
The flexible flatfoot combined with short Achilles tendon is the 25% of cases in adults and a smaller percentage in children and can be a cause of malfunction of the foot. The gait of some children on tiptoe (ballet dancer walking), which continued for long time may be a clinical point being short Achilles tendon and should be evaluated by the specialist Orthopaedic and not only by the pediatrician.
The most common cause of a rigid flatfoot is a tarsal coalition. The most common sites for a coalition are between the calcaneus and vavicular and between the talus and calcaneus. The synostosis causes increased load in the neighboring joints and creates pain and premature wear. These symptoms develop in adolescence or later.
Other causes of rigid flatfoot include, congenital vertical talus, juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, septic arthritis, and traumatic arthritis following intra-articular fracture of the subtalar joint.
CAUSE
Creating and maintaining the arch defined by the shape of the bones and the general laxity of the body ligaments. Some children are born with loose joints in the body without this constituting a pathological entity and has inherited basis.
Children are very often has flexible pes planovalgus.
The tarsal coalitions (middle part of the foot), is often familial, may appear in one or both legs and occur in both sexes equally.
There are rare forms of flat foot due to neurological diseases the child as cerebral palsy, polio, or syndromes such as Down's syndrome, Marfan syndrome in which the joint are pathological lax.
CLINICAL EXAMINATION
Role of Orthopaedic surgeon is to recognize the cause of flat foot in the child. The clinical examination for the detection and separation of flexible form from the rigid form or a type with short Achilles tendon is the cornerstone for the design of the treatment plan for the child. In case of suspected neurological disease the child should be evaluated by a specialist pediatric neurologist.
The clinical examination of the foot helps the Orthopaedic surgeon separate the flexible or stiff nature of flat foot
Flexible flat foot with soft tissue protrusion (arrow)
The inclination of the calcaneus outwardly is established with the person overview from behind (calcaneus valgus)
X-RAY
Plain radiographs of the foot with the child upright, may stand feet on the ground, gives information on the situation of the foot and exploring existence synostosis.
Radiological control with the person upright, highlights the nature and seriousness of the problem
FOOT ANALYSIS
After the age of 4-5 years should be done in the child foot analysis - static and dynamic - to obtain information on how loaded the feet, the pressure points on the surface of the plantar surface and how much pressure is applied to different parts of foot (heel, metatarsal heads, etc).
The foot analysis constitute a database (measure) for comparison of future examinations and Orthopaedist can evaluate the progress of each therapeutic approach if course necessary, or worsening of the clinical picture of the small patient over time.
Mechanical foot analysis
Static feet analysis
Dynamic feet analysis (walking analysis)
Mechanical foot analysis with special foam
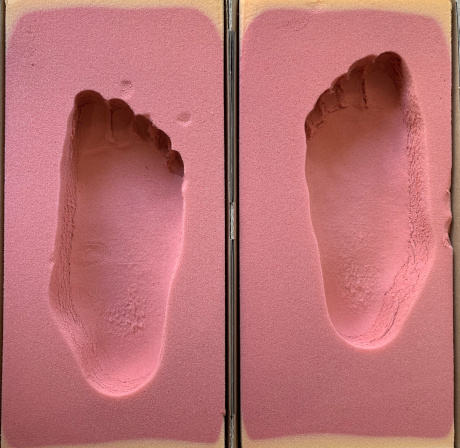

Severe flat feet with valgus orientation of the heel in boy 4 years old
Combining electronic and mechanical feet analysis is a complete system of evaluation of the child's feet, whose data will be used to create special insoles or special footwear.


