STEM CELLS AND ARTICULAR CARTILAGE DAMAGE
Articular cartilage lesions ar a debilitating disease resulting in fibrillation and subsequent degradation which can also involve the subchondral bone.
The damage to the articular cartilage is a common clinical entity not only in the elderly but also young people . At younger ages usually due to injuries during sporting activities and in diseases such as osteochondritis dissecans (incomplete perfusion in a section of bone resulting detachment of the articular cartilage ).
At older ages appears in the form of degenerative disease - primary osteoarthritis.
After injury to the joint or the appearance of osteochondritis dissecans , the remaining gap of the cartilage creates symptoms of pain , swelling and mechanical engagement , resulting in portions dissociated cartilage irritating articular synovium - synovitis - and interposed between the articular surfaces .
These symptoms usually lead to the withdrawal of the individual from physical activities.
If cartilage damage remain without treatment will lead to premature degeneration of the joint - secondary osteoarthritis.
Therapy with autologous stem cells represents a promising new perspective on the rapidly evolving field of regenerative medicine.
One limiting factor in the repair of these defects is the well-known low intrinsic regeneration potential of cartilage.
Therapeutic properties of mesenchymal stem cells are due not only to their capacity to differentiate but also to their ability to release growth factors that regulate the immune response in a paracrine manner.
Initially Orthopaedic Surgeon take a sample of adipose tissue or bone marrow of the patient, tissues containing abundant stem cells without the patient needing to be hospitalized in the clinic. Then it is sent to a special regenerative biotechnology company where the stem cells are cultured and expanded for 5-6 weeks.
Stem cells have the ability to maintain the mitotic capacity without significant loss of specific biomolecular characteristics during their culture in vitro and are capable of differentiating into multiple mesenchymal phenotypes that other cells such as chondrocytes and osteocytes.
Adipose derived stromal cells represent valid candidates to promote cartilage healing due to their ability to release biologically chondrogenic active factors, such a transforming growth factor – β1 (TGF-β1), and bone morphogenetic protein 4 (BMP-4), anti-fibrotic and anti-apoptotic factors and possible ability to decreasing local inflammation in several musculoskeletal disease.
Recently we apply the direct injection of autologous stem cells derived from bone marrow of the patient himself. This method has the great advantage of direct application of stem cells ie without waiting four weeks of culturing these to the affected joint.
THE PROCEDURE IS AS FOLLOWS:
With trocar (trocar) receive 60 cc bone marrow from the region of the iliac crest. This material is placed in a special stem cell isolation unit and in 30 minutes the Orthopaedic surgeon been in the hands of the accumulated stem cells which can inject the affected joint.
During this procedure the patient is in light sedation (anesthetic sedation), to avoid the sensation of pain during making of autologous stem cells from the posterior or anterior iliac crest of the patient.
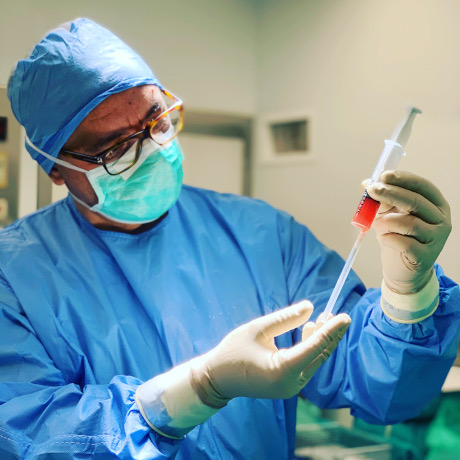
The nurse prepare the special trocal for bone marrow suction (from pelvis)
Bone marrow suction with special trocar from the patients pelvis
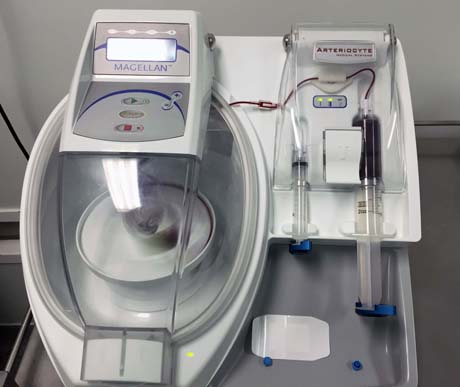
Special equipment to isolate the stem cells from the patients bone marrow'
The stem cells is ready (small syringe)
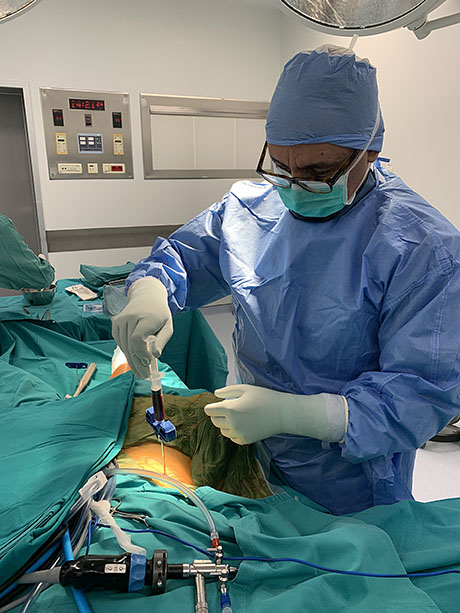
The autologous stem cells injected in the knee with osteochondritis dissecans (after arthroscopy)
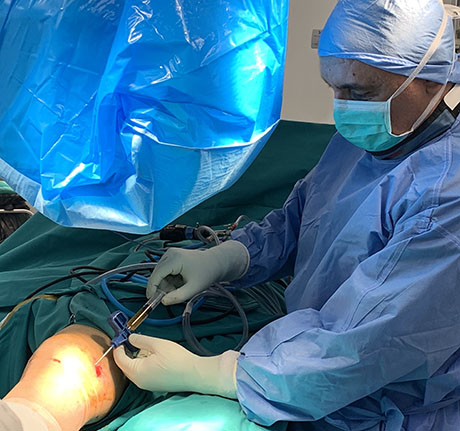
The special needle is inside in arthritic hip joint under fluoroscopic vision
Fluoroscopic vision, the needle is inside the hip joint
Stem cell injection
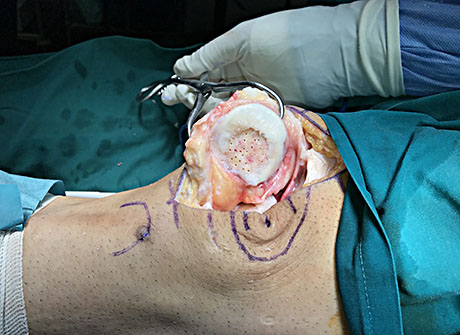
Articular cartilage damage (Outerbridge VI stage), Curetage in the base of the lesion and nanofracture
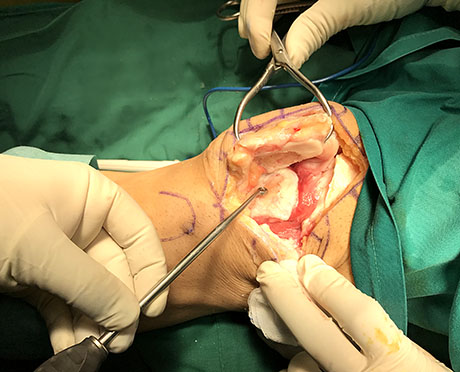
Severe femoral trochlea arthritis, (Outerbridge VI stage). Curetage and preparing for autologous stem cells implantation
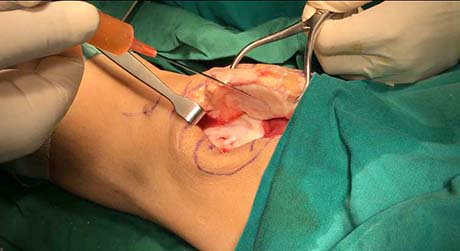
Autologous stem cells implantation in the cartilage lesion of the patella and trochlea
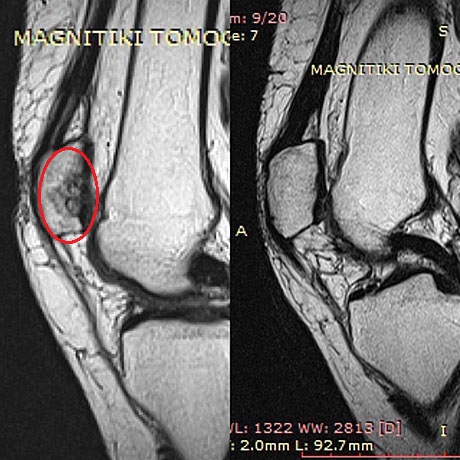
Woman 59 years old with severe damage of the patellar articular cartilage. Autologous bone marrow stem cells with collagen (AMIC technique), before and two years postop
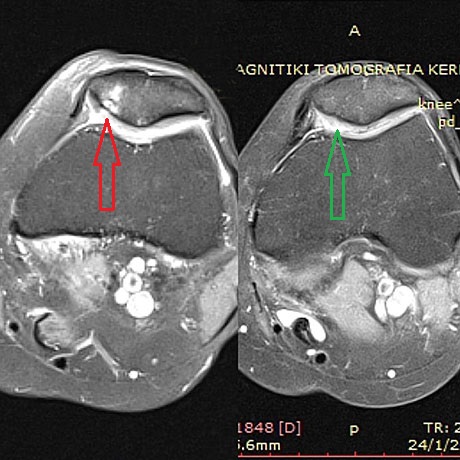
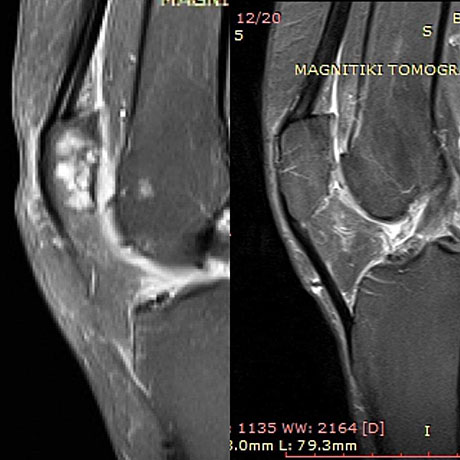
The same patient.
Then Orthopaedic Surgeon, depending on the condition of the patient can :
1. with arthroscopic surgery to place the stem cells at the defect of articular cartilage as in traumatic focal lesions or osteochondritis dissecans in young ages. The act creates new cartilage regeneration conditions . The patient will remain in the clinic for 24 hours and the recovery will last 6 weeks.
2. to inject directly into the affected joint ( injection) , in cases of degenerative osteoarthritis in older ages , without the patient needing to be hospitalized in the clinic.
The patient feels the relief of joint pain , improve mobility and upgraded in this way the quality of life.
The scope of stem cell therapy in Orthopaedics expands daily as the application of the method in osteonecrosis of the femoral head ( avascular necrosis ) in nonunions - fractures which did not succeed in their union in bone defects in combination with autologous grafts Ms. marking a a new minimally invasive therapeutic horizon , stimulating the self-reconstruction and self-renewal mechanisms of the human organization.

Published in Greek ELLE magazine (2014)