EVERY HUMAN IS DIFFERENT
George D. Goudelis MD. PhD.
Orthopaedic Surgeon – Doctor of the University of Athens.
Specialized in Robotic and Arthroscopic Surgery and Orthopaedics
Adult and Pediatric Sports Medicine, Heidelberg, Germany.
Director of ArthroHeal Clinic, Thessaloniki.
Doctor of YMCA Men’s Basketball Team

Modern orthopedics
FASTER, PERSONALIZED, EFFICIENT TREATMENT!
Evolution in Orthopaedics are impressive. In almost every joint, in every bone, ligament and muscle system of the human body such as the knee, hip and foot, we are able now to give therapeutic solutions more efficient and more sustainable.
Understanding the different needs of each patient by the athlete, computer operator until elderly man, leads to different conservative or invasive treatment regimen.
Disease + Treatment
Knee
Hip
Spine
Foot
Hand
Shoulder









Evolution
MODERN SCIENTIFIC ADVANCEMENTS IN ORTHOPAEDICS
ORTHOPEDIC SPORTS MEDICINE: Movement is life.
"Man ages from his joints" Maintaining the health of the musculoskeletal system contributes to maintaining a consistently good clinical picture. Exercise prevents basic diseases such as osteoporosis and sarcopenia, protects joints from osteoarthritis...

Persona Knee Arthroplasty
One of the most important developments in the history of Orthopedics is the total replacement of the knee joint with special materials. Today, with the help of electronic technology and surgical expertise,...

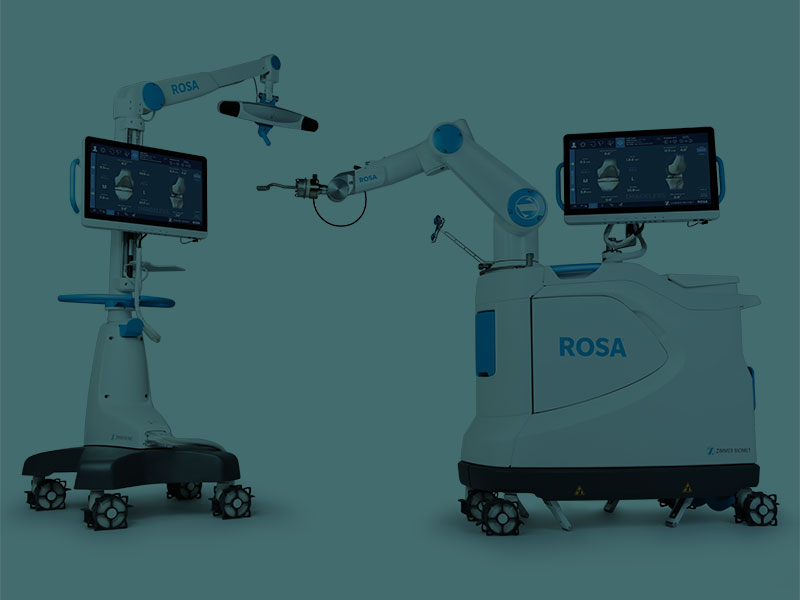
ROSA ROBOTIC KNEE ARTHROPLASTY
The new system ROSA ROBOTICS, is the most modern achievement of robotic technology in the field of Orthopedic surgery for the treatment of severe knee arthritis (osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, post-traumatic arthritis). ROSA...
AUGMENTED REALITY KNEE ARTHROPLASTY
Russian patient speak about the new computer assisted knee arthroplasty experience New sophisticated applications of electronic technology in recent years have entered in medicine, creating a new landscape of possibilities for the physician...

HIP ARTHROSCOPY
At present, hip arthroscopy arouses a very considerable interest and it is one of the great Orthopaedic surgery’s innovation of resent years. Hip has been the last big joint that explored with arthroscopic...

AUTOLOGOUS CHONDROCYTE IMPLANTATION – STEM CELLS IMPLANTATION
IMPLANTATION Injuries to joint surfaces can result from acute high-impact or repetitive shear and torsional loads to the superficial zone of the articular cartilage architecture. The use of autologous chondrocyte implantation is promising...

Personalized High Precision Knee Arthroplasty
Using the Persona® Knee System
Application of Zimmer Biomet’s advanced Persona® Knee System total knee arthroplasty system, with personalization based on the anatomy and functional requirements of each patient. This system offers broad compatibility with different skeletal types, ensures optimal reproduction of natural knee kinematics and contributes to faster recovery, reduced postoperative complications and improved mid- to long-term outcomes.


Sports medicine
“My involvement with sports medicine began with my active participation in the Athens University Clinic of Orthopaedics (KAT), and especialy in sports medicine clinic where I specialized in orthopaedics with emphasis on arthroscopic surgery and sports injuries. The highlight came with my fellowship at the ATOS Clinic in Heidelberg, an ISAKOS-approved sports medicine specialist centre, where I specialised in advanced techniques in arthroscopic knee, ankle and sports injury surgery. My daily contact with athletes has taught me to stand by them consistently, not only to get them back on the field quickly and safely, but also to build a relationship of prevention and respect for their bodies.”
George D. Goudelis M.D. PhD.
Anterior cruciate ligament rupture
CASE REPORT
The anterior cruciate ligament is one of the four major ligaments of the knee. It contributes to its stability and smooth functioning. The rupture of the ligament is the most common ligamentous injury of the joint and occurs mainly in athletes during their activities but is also found in traffic accidents and industrial accidents. New minimally invasive arthroscopic techniques are applied from childhood with ligament injury problems, minimizing pain and speeding up the rehabilitation period.




